Unlocking Market Opportunities Through Fundamental Analysis
Finding undervalued stocks is one of the most effective ways to build long-term wealth in the stock market. Fundamental analysis provides traders and investors with the tools to assess a company’s true value, allowing them to make informed decisions about potential investments. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, mastering this approach can give you an edge in identifying stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value.
At EPIQ Trading Floor, we help traders refine their stock-picking strategies with expert insights, live trade signals, and one-on-one coaching. If you’re ready to take your trading to the next level, use code “BLOG” at checkout for 10% off and enjoy a risk-free 3-day trial—cancel anytime within 72 hours without being charged. Join now.
What Is Fundamental Analysis?
Fundamental analysis is a method used to evaluate a stock’s intrinsic value by analyzing financial statements, industry trends, and macroeconomic factors. Unlike technical analysis, which focuses on price action and chart patterns, fundamental analysis looks at the company’s financial health, competitive position, and future growth potential. Investors use this strategy to determine whether a stock is overvalued, fairly valued, or undervalued compared to its true worth.
By studying key financial metrics, company earnings, and industry trends, traders can pinpoint stocks that may be poised for future growth. Buying undervalued stocks before the broader market recognizes their potential can lead to significant gains over time.
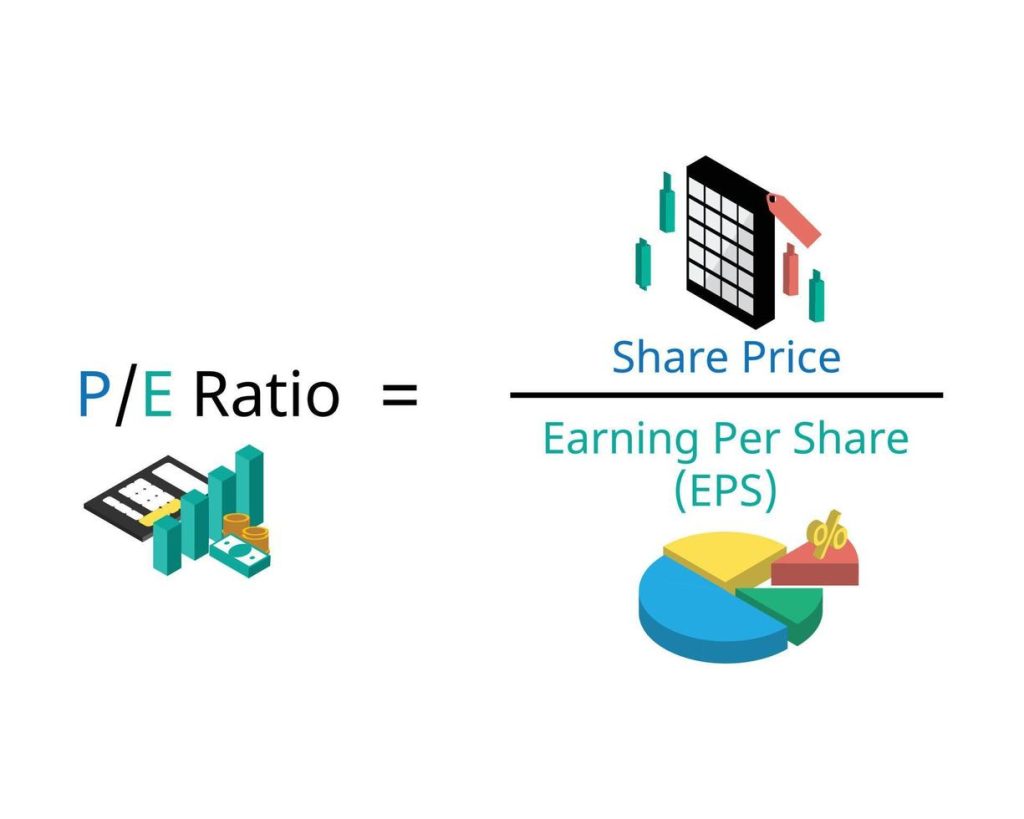
Key Metrics for Identifying Undervalued Stocks
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share (EPS). A low P/E ratio relative to industry peers may indicate that a stock is undervalued. However, it’s essential to analyze this metric in context, as different sectors have different average P/E ratios.
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The P/B ratio measures a stock’s price relative to its book value, which represents the company’s assets minus liabilities. A P/B ratio below 1 suggests that a stock is trading for less than the value of its net assets, signaling a potential buying opportunity.
Earnings Per Share (EPS) Growth
EPS represents a company’s profitability per outstanding share. Consistent EPS growth over time is a positive sign, indicating that a company is increasing its earnings, which can lead to higher stock prices in the future.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE measures a company’s profitability in relation to shareholder equity. A high ROE suggests that management is efficiently using capital to generate profits, making it an important indicator of a company’s financial strength.
Debt-to-Equity (D/E) Ratio
The D/E ratio compares a company’s total debt to its shareholders’ equity. A high D/E ratio may indicate financial instability, whereas a low D/E ratio suggests that the company is not overly reliant on debt to finance its operations.
Free Cash Flow (FCF)
FCF represents the cash a company generates after accounting for capital expenditures. A company with strong free cash flow has more financial flexibility to reinvest in growth, pay dividends, or reduce debt, making it a good candidate for long-term investment.
Understanding Intrinsic Value and Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
One of the most powerful tools in fundamental analysis is Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis. This method estimates a company’s intrinsic value by projecting future cash flows and discounting them to their present value. If the DCF valuation indicates that a stock is worth significantly more than its current market price, it may be undervalued and worth considering as an investment.
However, DCF analysis requires careful assumptions about a company’s future revenue growth, operating margins, and risk factors. Investors often use multiple valuation models alongside DCF, such as price multiples and relative valuation, to confirm their findings.
Identifying Market Inefficiencies and Buying Opportunities
Stocks can become undervalued due to several market factors, including temporary economic downturns, industry-wide corrections, or negative sentiment driven by short-term news events. Some of the best buying opportunities arise when fundamentally strong companies experience short-term stock price declines due to external factors unrelated to their long-term business prospects.
For example, during economic recessions, even high-quality companies may see their stock prices decline as investors panic and sell off their holdings. Traders who can recognize market overreactions and identify companies with strong fundamentals can buy these stocks at discounted prices before they recover.
According to CNBC, historical data shows that value stocks—those trading at lower price multiples—have historically outperformed growth stocks during periods of rising interest rates. This highlights the importance of identifying undervalued stocks at the right time. (Source).
A recent study from Bloomberg also found that companies with strong balance sheets and low debt ratios tend to outperform during market downturns, reinforcing the value of fundamental analysis in stock selection. (Source).
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Searching for Undervalued Stocks
While fundamental analysis can be a powerful tool, traders should be aware of common mistakes that can lead to poor investment decisions. One key mistake is relying solely on low valuation metrics without considering a company’s future growth potential. Just because a stock has a low P/E or P/B ratio doesn’t necessarily mean it’s a good investment—it could be a sign of a struggling company with declining revenue.
Another mistake is ignoring macroeconomic conditions and industry trends. Certain sectors, such as technology or healthcare, may have higher average valuation multiples due to their growth potential. Comparing a tech stock to a utility stock using the same valuation metrics can lead to misleading conclusions.
Finally, failing to diversify investments can expose traders to excessive risk. While focusing on undervalued stocks can be profitable, it’s important to maintain a well-balanced portfolio to mitigate potential losses.

Conclusion: Improve Your Trading With EPIQ Trading Floor
Mastering fundamental analysis is essential for traders looking to identify undervalued stocks and capitalize on long-term growth opportunities. By analyzing key financial metrics, understanding intrinsic value, and recognizing market inefficiencies, traders can build a solid foundation for making informed investment decisions.
At EPIQ Trading Floor, we provide exclusive trade signals, in-depth market insights, and one-on-one coaching to help traders navigate the stock market with confidence. Sign up for a risk-free 3-day trial and use code “BLOG” at checkout for 10% off. Join today and take your trading skills to the next level.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Trading stocks, options, and other financial instruments carries risks, and you should conduct your own research or consult with a professional before making any trading decisions.









Responses